Pandas
: 구조화된 데이터를 효과적으로 처리하고 저장
: Array 계산에 특화된 NumPy를 기반으로 설계
Series
: numpy의 array가 보강된 형태
: Data와 Index를 가지고 있음

Series는 값을 ndarray형태로 가지고 있음
print(type(data)) --> <class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>
print(type(data.values)) --> <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
dtype인자로 데이터 타입을 지정할 수 있음
data = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4], dtype = "float")
print(data.dtype) --> float64
인덱스를 지정할 수 있고 인덱스로 접근 가능
data = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4], index = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])
data['c'] = 5 # 인덱스로 접근하여 요소 변경 가능
Dictionary를 활용하여 Series 생성 가능
population_dict = { 'china': 141500, 'japan': 12718, 'korea': 5180, 'usa': 32676 }
population = pd.Series(population_dict)
DataFrame
: 여러 개의 Series가 모여서 행과 열을 이룬 데이터
gdp_dict = { 'china': 1409250000, 'japan': 516700000, 'korea': 169320000, 'usa': 2041280000, }
gdp = pd.Series(gdp_dict)
country = pd.DataFrame({ 'gdp': gdp, 'population': population })
Dictionary를 활용하여 DataFrame 생성 가능
data = { 'country': ['china', 'japan', 'korea' , 'usa'], 'gdp': [1409250000, 516700000, 169320000, 2041280000], 'population': [141500, 12718, 5180, 32676] }
country = pd.DataFrame(data)
country = country.set_index('country')
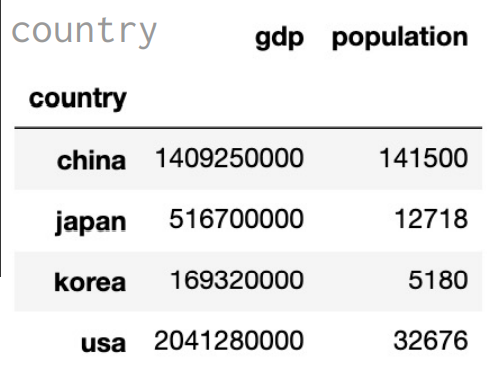
DataFrame 속성 확인
print(country.shape) # (4, 2)
print(country.size) # 8
print(country.ndim) # 2
print(country.values) # [[1409250000 141500] [ 516700000 12718] [ 169320000 5180] [2041280000 32676]]
DataFrame의 index와 column에 이름 지정
country.index.name = "Country" # 인덱스에 이름 지정
country.columns.name = "Info" # 컬럼에 이름 지정
print(country.index) # Index(['china', 'japan', 'korea', 'usa'], dtype='object', name='Country’)
print(country.columns) # Index(['gdp', 'population'], dtype='object', name='Info')
데이터 프레임 저장 및 불러오기
country.to_csv("./country.csv") # csv 저장
country.to_excel("country.xlsx") # excel 저장
country = pd.read_csv("./country.csv")
country = pd.read_excel("country.xlsx")
데이터 선택 및 변경하기(Indexing/Slicing)
.loc: 명시적인 인덱스를 참조하는 인덱싱/슬라이싱
country.loc['china'] --> 인덱스가 중국인 값만 가져오라
country.loc['japan':'korea', :'population'] --> 슬라이싱(인덱스, 컬럼)
- 구체적인 인덱스의 이름을 모를 때
.iloc: 파이썬 스타일의 정수 인덱스 인덱싱/슬라이싱 ex) 이름 모를 때: 그 집 첫째 딸, 둘째 딸
country.iloc[0] --> 인덱싱
country.iloc[1:3, :2] --> 슬라이싱 [행 / 열]
- 컬럼명을 활용하여 DataFrame에서 선택 가능
country['gdp'] --> (컬럼) Series
country[['gdp']] --> DataFrame
- Masking 연산이나 query함수를 활용하여 조건에 맞는 DataFrame 행 추출가능
country[country['population'] < 10000] --> masking 연산
query안에 쌍따옴표
country.query("population > 100000") --> query 함수 활용
- Series는 numpy array처럼 연산자 활용 가능
gdp_per_pop = country["gdp"] / country["population"] # gdp에서 population을 나눠 1인당 gdp를 구합니다.
country["gdp per capita"] = gdp_per_pop
- 리스트로 추가 or 딕셔너리로 추가
df = pd.DataFrame(columns = ['이름', '나이', '주소'])
df.loc[0] = ['길동', '26', '서울'] --> 리스트로 데이터 추가
df.loc[1] = {'이름':'철수', '나이':'25', '주소':'인천'} --> 딕셔너리로 데이터 추가
df.loc[1, '이름'] = '영희' --> 명시적 인덱스 활용하여 데이터 수정
- Not a Number값으로 초기화 한 새로운 컬럼 추가
df['전화번호'] = np.nan
df.loc[0, '전화번호'] = '01012341234'
- DataFrame에서 컬럼 삭제 후 원본 변경
df.drop('전화번호', axis=1, inplace=True)
--> axis=1: 열 방향, axis=0: 행 방향
--> inplace = True: 원본변경 O / inplace = False: 원본변경 X